axial compression test lumbar|tensile test vs compression : manufacturing Midline back pain is the hallmark symptom of lumbar compression fractures. The pain is axial, non-radiating, aching, or stabbing in quality and may be severe and disabling. The location of . Carros usados França. OOYYO - Comparador de preços de carros - 3.725.443 anúncios de carros no último mês. Preço. Carros usados França. 15 de 780.712 Resultados. OOYYO .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBClique para se divertir
what is triaxial compression test
Midline back pain is the hallmark symptom of lumbar compression fractures. The pain is axial, non-radiating, aching, or stabbing in quality and may be severe and disabling. The location of . Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures are very common fragility fractures of the spine that affect up to 50% of people over 80 years old. Diagnosis can be made with . compression of lower lumbar nerve roots (L4-S1) important to distinguish from hamstring tightness. considered positive if symptoms produced with leg raised to 40°. crossed straight leg raise. performing straight leg raise .In particular, we propose that an important variable potentially contributing to continued symptoms with testing is axial compression. Axial compression of the lumbar region is operationally .
Vertebral compression fractures (VCFs) of the spinal column occur secondary to an axial/compressive (and to a lesser extent, flexion) load with resultant biomechanical failure . Common sources of axial LBP include the intervertebral disc, facet joint, sacroiliac joint, and paraspinal musculature, whereas common sources of radicular pain include a .
notch angle in charpy impact test
Axial compression of the lumbar re-gion is operationally defined as loading applied parallel to the long axis of the spine, such that the tissues are approxi-mated.25 There is evidence to .Compression fractures are usually caused by an axial load on the anterior part of the vertebrae. Due to this vertical force, this specific part of the vertebrae will lose height and will become wedge-shaped. INTRODUCTION. It is estimated that up to 84 percent of adults have low back pain at some time in their lives [1,2]. For many individuals, episodes of back pain are self-limited. The disc resists axial compression and tension, lateral and antero-posterior shear, and axial rotation. The shape of the disc in the lumbar spine is such that the lordotic curvature is maintained by the greater height .
The effect on the lumbar spine of axial compression has concentrated on the assessment of changes in DCSA . Willen et al. assessed the effects of axial compression in three patient groups, those with chronic low . Dynamic axial compression bending test. Six (6) Memory Metal Spinal System constructs and titanium 5.5 mm diameter Moss Miami constructs were tested in axial compression bending fatigue using a servo hydraulic .
Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures are very common fragility fractures of the spine that affect up to 50% of people over 80 years old. Diagnosis can be made with lateral radiographs. Determining the acuity of a fracture requires an MRI or bones scan.These types of back surgery are reserved for pain secondary to compression of the spinal nerve roots or sac. See Lumbar Radiculopathy The surgical and non-surgical treatment of chronic axial back pain (e.g. lasts more than six weeks), is somewhat controversial and .The weight of the trunk alone in an upright posture is associated with axial compression and decreased intervertebral disc height. 2,12,13,15,21,32,33 Paraspinal and abdominal muscle contraction, even during low-load tasks and postures, has been shown to increase spinal compression, particularly in people with LBP. 1,3,7–9,17,22,27 Although . Axial LBP attributed to the lumbar facet joints is estimated to affect approximately 15% to 30% of patients. 6,71,72 Although numerous studies have attempted to identify the historical and physical examination findings associated with lumbar facet pain, no discrete set of clinical markers has been delineated. 47 However, the onset of lumbar .
The flexion pattern contains compression fractures and axial burst fractures. The extension pattern, which contains flexion/distraction (often called a chance fracture). . SCT is a sensitive diagnostic test for the identification of spinal fractures. A more recent study by Ang et al . ↑ Andrew L Sherman et al. “Lumbar Compression .
combined changes lead to a narrowing of the spinal canal and compression of the neural elements. Associated conditions. degenerative spondylolisthesis. . cross sectional area <100mm2 or <10mm A-P diameter on axial CT . . Valsalva test. radicular pain not worsened by Valsalva as is the case with a herniated disc.
pressive load on the lumbar spine.1,17,22 Regardless of the specific mechanism, the cumulative effects of axial compres-sion eventually may lead to LBP, due to increased mechanical stress on multiple structures of the lumbar region.1,16,20 Several strategies may be used to decrease axial compression of the lum-bar spine. While lumbar spine axial compression loading in HBMs and ATDs as high as 5000 N has been predicted in reclined simulations (Gepner et al. Citation 2019, Ostling et al. Citation 2021), the study by Tushak et al. (Citation 2022) suggests that axial compression of approximately 4500 N will carry a 50% risk of vertebral body fracture. Since this .Chronic compression develops over months to years. It is commonly caused by. Bony protrusions into the cervical, thoracic, or lumbar spinal canal (eg, due to osteophytes or spondylosis, especially when the spinal canal is narrow, as occurs in spinal stenosis) Compression can be aggravated by a herniated disk and hypertrophy of the ligamentum .
what is deep neck compression
Objective: The goal of this study was to evaluate the effect of axial compression, employed with a follower-load mechanism, on the response of the lumbar spine in flexion and extension bending. A Spurling’s test is a compressive test for foraminal compression. The patient will lean their head all the way back, and the clinician will apply axial compression (push down on the head). If the test is negative, it can be done with rotation to the left and right. . In the thoracic and lumbar spine, axial MRI is helpful in recess and .
each lumbar spinal section (L1–L4) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was used to grade disk degeneration of the motion segments employed. Segments were loaded with an axial compressive force of 1600 N. Subsequently, anterior shear load was applied with a con-stant rate of 2.0 mm/min on the casting mold containing the cranialStudy design: In vivo study using young healthy volunteers, CT scan, and an axial compression device. Objective: This study was conducted to evaluate the test-retest repeatability of the measurements of sagittal alignment and disc height of the lumbar spine with and without an axial compression device in the supine position. Summary of background data: Dynamic radiologic . Loads on lumbar vertebrae during hang power clean cycle. (a) Shear force on L1; (b) Axial compression on L1; (c) Bending moment in sagittal plane on L1; (d) Shear force on L5; (e) Axial compression on L5; (f) Bending moment in sagittal plane on L5. For all the data reported, vertical dotted lines indicate completion of the second pull. Lumbar interbody fusion (LIF) is a common procedure used to treat a variety of spinal pathologies, with over 90,000 performed in the U.S. per year (Goz et al., 2014).Four main surgical approaches have been developed for LIF procedures (Fig. 1).Anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF) allows for anterior access to the disc space while avoiding the posterior .
Axial T1-images are used to search for extraforaminal stenosis by showing an obliteration of the normal interval of fat between the disc and the nerve root. . it is recommended to use the gait-loading test which is a provocation test . The lumbar extension . becomes narrowed. If the narrowing is substantial, it can cause compression of the . The setup for biomechanical testing (A) used to test spinal segments in flexion-extension and lateral shear (B), lateral bending and anteroposterior shear (C) and axial rotation and axial compression-decompression (D). Biomechanical testing protocol.
To evaluate the effects of the device, these parameters under axial loading and lying down conditions were compared statistically using the paired t test. Although spinal length was significantly .
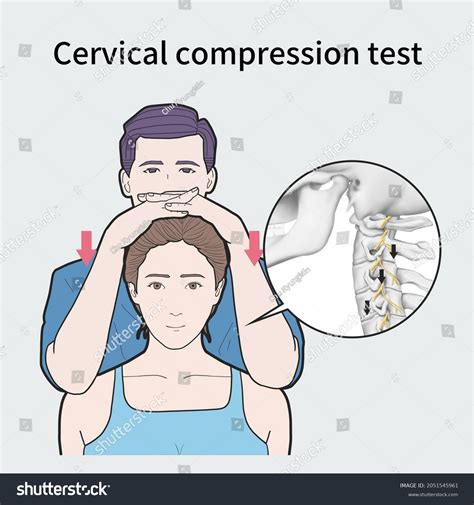
foraminal compression test that is specific, but not sensitive, in diagnosing acute radiculopathy . and then applying and axial load (downward pressure on the head) test is considered positive if pain radiates into the ipsilateral arm when the test is performed for 30 seconds . for cervical spinal cord compression and myelopathy. test is .Load testing after PLED of spine from L4-L5. In the axial neutral position 400 N axial compression loads were applied to each specimen in both groups (Figure 1).A specially designed fixture used .
It’s also called the Spurling compression test or Spurling maneuver. Cervical radiculopathy occurs when a nerve in your neck is pinched near the area where it branches away from your spinal cord. According to one source, Spurling originally described the test as lateral bending and axial compression. (1) Reproduction of radicular pain and symptoms is measured. Six variations of the test are described in the literature: . This guideline provides recommendations related to management of patients and cardiovascular risk post-spinal cord .The test is based on stretching of the nerves in the spine. Crossed Straight Leg Raise Test (Crossed Lasègue test): A test for the containment and exclusion of lumbar radiculopathy. For the cross straight leg raising test a pooled sensitivity was 0.29 (95% CI 0.24-0.34), pooled specificity was 0.88 (95% CI 0.86-0.90) (LOE 1A). The test is .
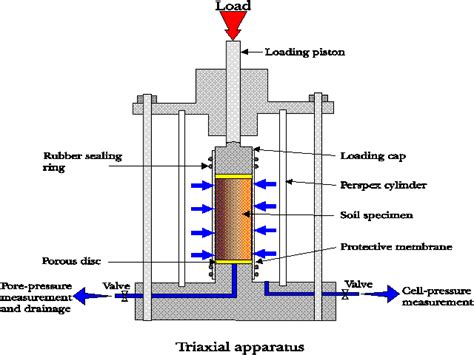
triaxial test on rock
Intervertebral Body Fusion devices are used to promote arthrodesis of a spinal motion segment, following disc degeneration. The implant acts as a support of the anterior column whilst the two vertebral discs grow together and fuse the spine. . TEST FIXTURE. For both the Axial-compression and Compression shear tests the same fixture is used .
tensile test vs compression
Rei dos Canais - Assista aos Melhores Canais ao Vivo Gratuitos
axial compression test lumbar|tensile test vs compression